Many people still do not understand what Cryptocurrency is like Bitcoin, this introduction will explain the most important thing about cryptocurrencies and when you have read it, you will know more about it than most other humans. Cryptocurrencies have captured the imagination of some, struck fear among others, and confused the rest of us.

How Did Cryptocurrencies Start?
Cryptocurrency, initially started as an educational concept, evolved into a revolutionary financial technology that has transformed various industries. The story begins with the advent of Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, introduced to the world in a whitepaper published by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto in October 2008.
Bitcoin's whitepaper, titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," proposed a decentralized digital currency that would enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. It was essentially designed to address the shortcomings of traditional financial systems, such as high transaction fees, slow settlement times, and centralized control.
Initially, Bitcoin gained traction within cryptography and computer science communities where enthusiasts were intrigued by the underlying technology, known as the blockchain, which served as a transparent and tamper-proof public ledger.

Damian Dovarganes/AP/Shutterstock
To further spread knowledge about cryptocurrencies, online forums and discussion platforms emerged. The most notable of these was the Bitcointalk forum, where developers, enthusiasts, and curious individuals could engage in discussions, share ideas, and exchange information about Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. These platforms played a pivotal role in fostering a sense of community and enabling knowledge sharing among early adopters.
As interest grew, educational resources and initiatives were established to facilitate learning about cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Online tutorials, forums, and blogs emerged, providing insights into the technical aspects of cryptocurrencies, mining, wallets, and security practices. Some early adopters even organized workshops and conferences to educate and discuss the potential applications and implications of cryptocurrencies in various fields.
Furthermore, academic institutions began recognizing the importance of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Universities around the world started offering courses on blockchain, cryptocurrency economics, smart contracts, and related subjects. Professors and researchers began conducting studies and publishing papers on various aspects of cryptocurrencies, fostering a deeper understanding of the technology.
Over time, the educational focus expanded beyond Bitcoin, with the emergence of alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) and blockchain platforms. Ethereum, for instance, introduced smart contracts, enabling developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) on top of its blockchain. This development further broadened the educational landscape, with new resources and research exploring the possibilities of decentralized finance, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and other innovative use cases.
The educational efforts surrounding cryptocurrencies have played a significant role in increasing awareness and adoption. As more individuals became educated about technology, they began to see the potential for disrupting traditional industries, such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
In conclusion, what started as an educational concept with the introduction of Bitcoin has evolved into a vast ecosystem of knowledge, resources, and applications surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. The continuous educational efforts have not only expanded understanding but also fueled innovation and adoption, transforming the way we perceive and interact with finance and various other sectors.
Simple Explanation of a Cryptocurrency
In layman's terms (for dummies) it is just limited entries in a database no one can change without fulfilling specific conditions. This may seem ordinary, but, believe it or not: this is exactly how you can define a currency. This is the same as your bank account, it is just entries in database tables with all your transactions, deposits and withdrawals. The system is completely decentralized, meaning there are no servers involved and no central controlling authority which closely resembles file sharing on peer-to-peer networks.
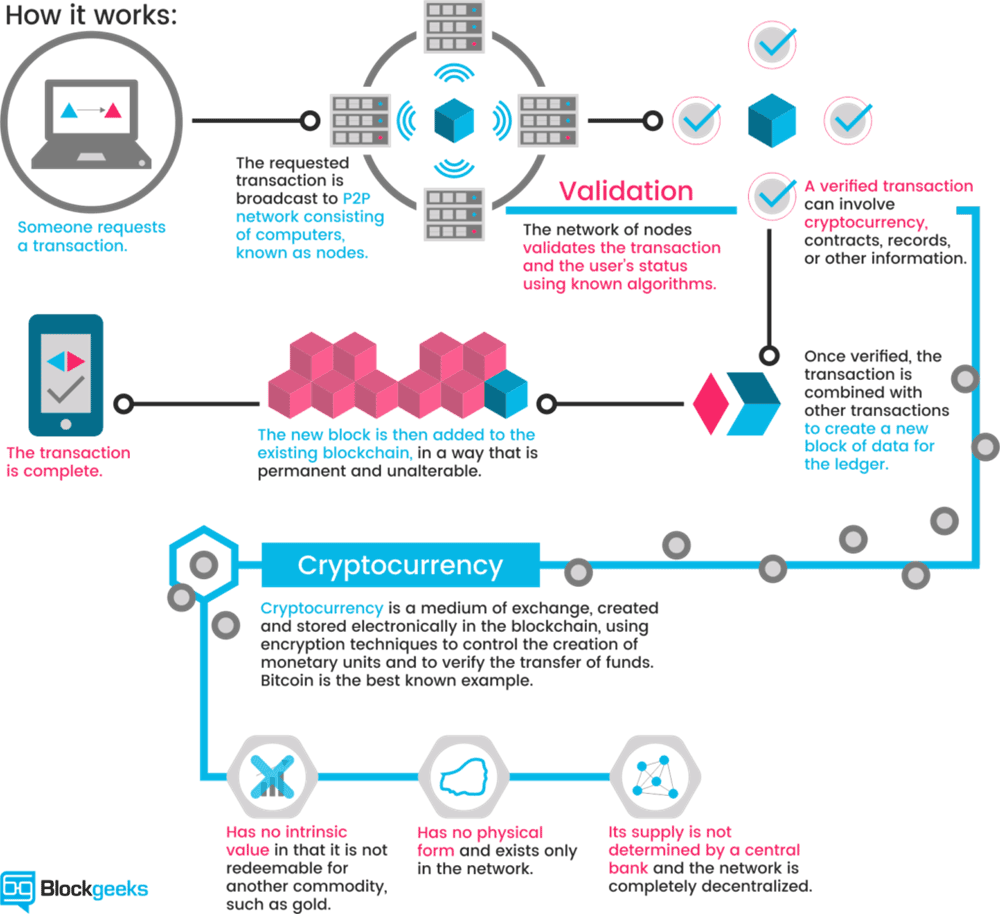
Image credits: BlockGeeks.com
How do The Miners Create Coins?
The databases used by cryptocurrencies use rules consisting of network peers and each peer has a complete historical record of all transactions for the customer's account. If Customer A wants to give Customer B some Bitcoins the transaction is completed using cryptography encryption so that the transaction is 100% secure and this is completed over a peer-to-peer network using basic P2P technology. As long as a transaction is unconfirmed, it is pending and can be forged.
When a transaction is confirmed, it is set in stone and it is no longer forgeable when this occurs it is part of an immutable record of historical transactions that is that part of the so-called blockchain. The only potential problem is that these transactions could be captured and the encryption broken by a new breed of quantum computers, but this is just my opinion.
Only the miners can confirm the transactions as this is their job, what they do is take the transactions and stamp them as valid and then spread them in the network and after the transaction has been confirmed by the miner, it is added to the database and all the nodes are updated in the blockchain.
Anyone Can Mine for Crypto Coins
Practically anybody can be a miner and since a decentralized network has no authority to delegate this task, a cryptocurrency needs some kind of mechanism to prevent one ruling party from abusing it. Satoshi set the rule that the miners need to invest some work in their computers, they need to solve problems with powerful computers and once the problem is solved they are rewarded with coins, but these days it is very hard to justify the financial returns with hardware and electricity costs for so few coins.
What is Blockchain Technology?
The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.
Blockchain technology is like the internet in that it has great robustness and by storing blocks of information that are identical across its network, the blockchain cannot be controlled by any single entity and has no single point of failure. It also solves the problem of transaction data entry manipulation, making it very safe.




